B. Leaf Blades
Syringa (lilac) prepared slides are examine.
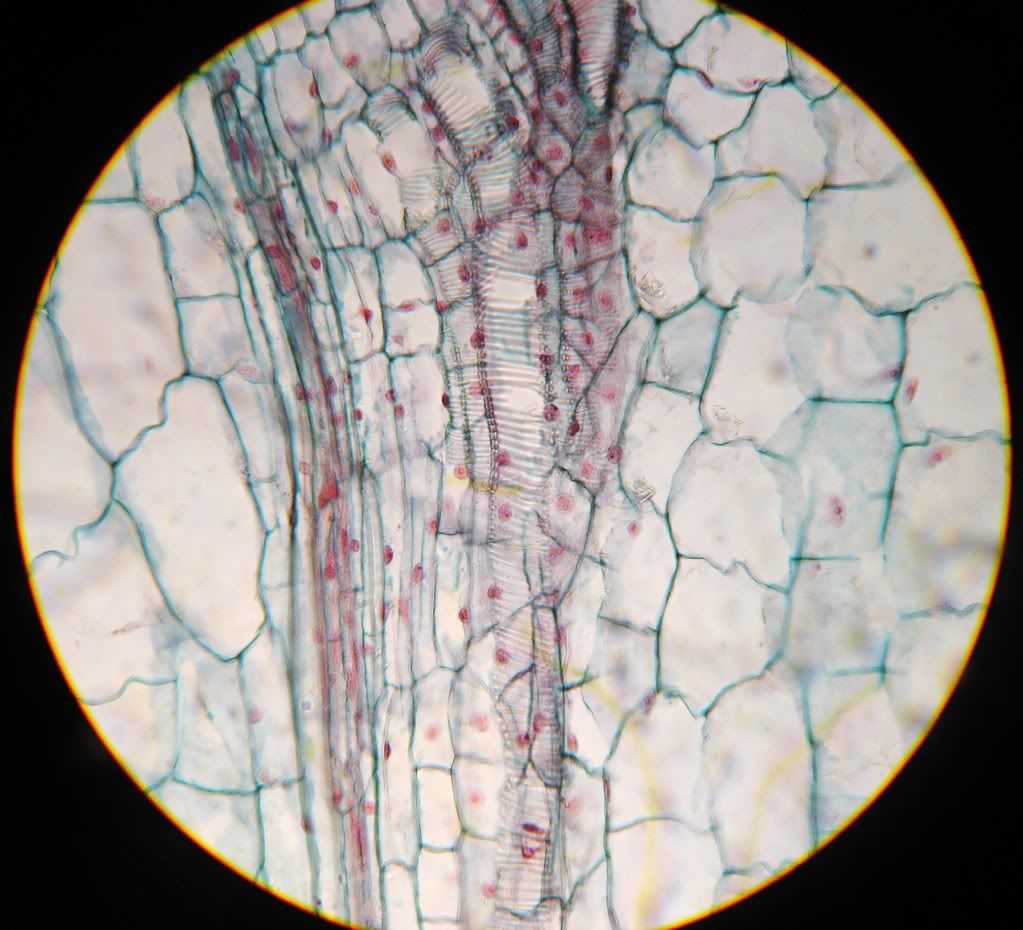
x10. Leaf of a lilac.
Mid-vein in a lilac leaf.
Note mid-vein is supported by cells with thickened walls above and below.
Variation in leaf blades:
1) Sun versus Shade Leaves
Prepared slides of leaves.
'Sun leaf'.
'Shade leaf'.
Compare to 'shade leaf', 'sun leaf' is thicker, with a smaller blade area and has more layer of palisade mesophyll, and more xeromorphic (maybe be affected by water relations) .
2) Maturity of plant
Plants like Hedera (English Ivy) have different leaf shapes in juvenile and mature stage.
Juvenile English Ivy has five-lobed leaves on the climbing vine.
Mature English Ivy has thicker leaves without lobes.
3) Habitat
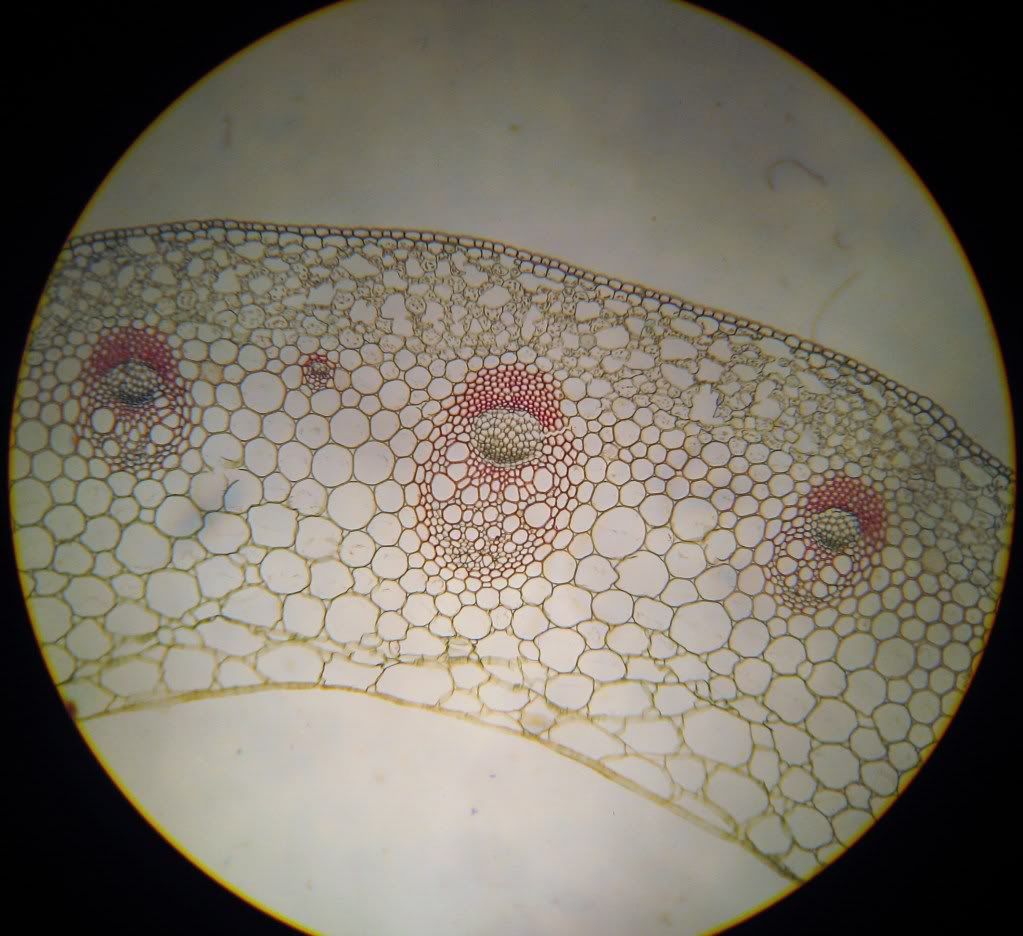
a) Mesophytic leaf - moderate habitats
- cuticle over epidermis
- more stomates on the lower leaf surface
- has adaxial palisade and abaxial spongy layers
Lonicera (honeysuckle) is one of the examples of plants that have mesophytic leaf.
Adaxial side of the lead.
Abaxial side of the leaf.
Mid-rid.
Note that there are both xylem and fibre.
Xylem has thinner cell wall compare to fibre.
Xylem is on the adaxial side of the leaf (below palisade mesophyll).
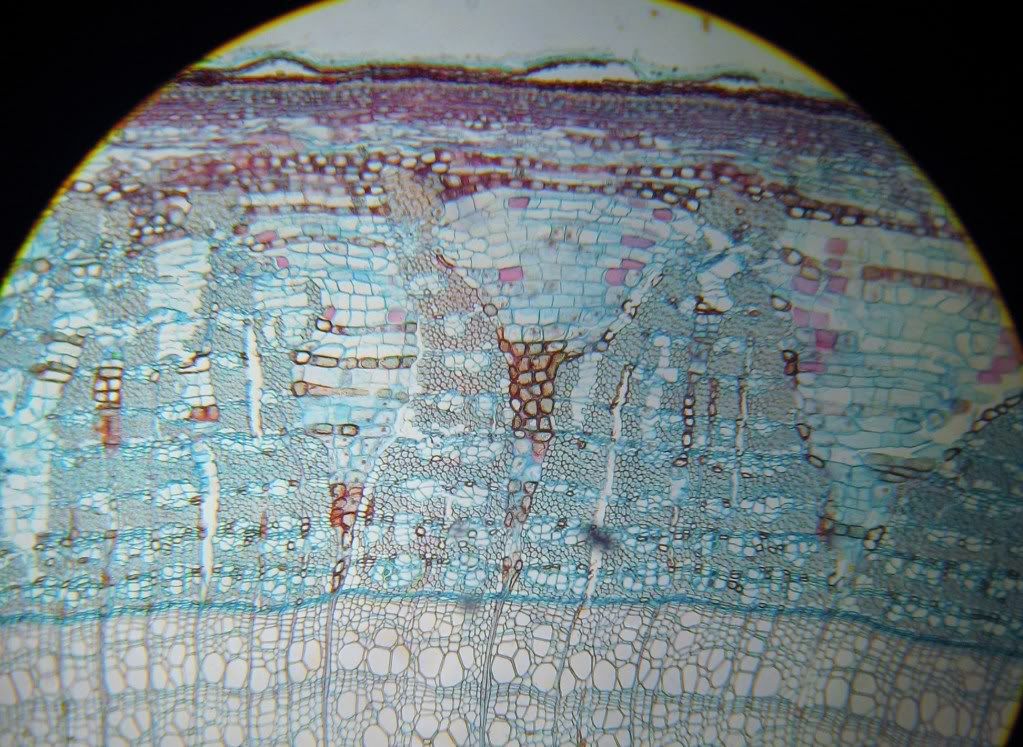
Corn also has mesophytic leaf.
Corn, like other grasses, the mesophyll does not differentiate into spongy and palisade layers.
Kranz anatomy:
The arrangement where there is a ring of
large, chloroplast-containing bundle-sheath cells
surrounding the vascular bundle.
(Not clear in this picture.)
b) Xerophytic leaf - Dry habitats
- thick cuticle
- sunken stomates
- more palisade layer
- less spongy layer
Cycad has compound leaves. So a cross-section of the leaflets does not have mid-rib, but mid vein.
Cycad leaf cross-section.
Adaxial side of the leaflet. x40.
Subsidiary cells overarch the stomata. x40.
3) Hydrophytic leaf - wet or submerged habitats
- submerged leaves lack stomates
- air cavities
Water lily leaf cross sections are examined.
The chloroplasts are red in colour.
Stoma only found in the adaxial surface of the lily leaf.
C. Trichomes
Adaxial side of the leaf of Viburnum rhytidophyllum.
The trichomes are found in the abaxial side of the leaf.
The trichomes are branching. What is the function? Protection and water regulation.
Larger magnification of the trichomes.
D. Leaf Appendagges
Stipules of the Begonia.
E. Shoot Modifications
1. Storage (water)
- parenchyma that has no chloroplasts; large, living, thin-walled, large vacuoles with watery or mucilaginous contents.
Peperomia glabella (wax privet peperomia) has multiple epidermis.
Multiple epidermis of large, thin-walled parenchyma cells that lack chloroplasts.
The oil sac are yellow in colour.
Aloe is a desert plant has water storage tissue within the photosynthetic tissues.
The colourless water storage tissue is slimy due to mucilage.
2. Protection
Thorn - stem
Spine - leaf
Prickle - epidermis
Citrus medicata (citron) has thorns.
Older citron tree.
The cross section of a thorn resemble that of the stem.
Euphorbia has spines (modified leaf).
Rubus (blackberry) has prickles.
No vascular bundle is observed in prickles.
3. Support
Peas' tendrils are modified leaf as they replace the terminal leaflets.
Passiflora (Passion flower) has modified branch as tendril. Its tendrils grow from the leaf base (axillary bud).
4. Vegetative reproduction
Kalanchoe form plantlets as a mean of vegetative reproduction.
5. Overcoming Nitrogen Deficiency: insectivourous plants
Sarracenia (Pitcher plant):
- nectar-secreting glands
-colouration
-downward-pointing hairs and waxy inner surface
-enzymatic fluid
Dionaea (Venus Flytrap): trigger hair.
Pink secretory cells that secrete digestive enzyme in Dionaea.
Drosera (sundew) has sticky mucilage and red-coloured to attract insects and the tentacles traps the insects when the insects touch the tentacles.
Utricularia vulgaris (Bladderwort)
I don't have a picture.
- Yee Sing